Numbers tell stories that intuition simply can’t. In the fast-paced world of e-commerce, the difference between thriving and merely surviving often comes down to how well you understand your data. But here’s the catch – not all Shopify stores are created equal, and the analytics that matter for a dropshipping operation might be dramatically different from those crucial to an inventory-based business.
I’ve worked with hundreds of Shopify merchants across both business models, and I’ve seen firsthand how proper analytics implementation can transform struggling stores into profitable powerhouses. The key? Knowing exactly which metrics deserve your attention and which are just noise.
For dropshippers, supplier reliability and product performance across multiple sources create unique data challenges. Meanwhile, inventory-based stores juggle stock levels, storage costs, and fulfillment efficiency metrics that dropshippers never have to consider. Your business model fundamentally changes which numbers should keep you up at night.
In this guide, we’ll explore how to harness Shopify’s analytics capabilities for both dropshipping and inventory-based stores. You’ll learn which KPIs matter most for your specific model, how to set up custom dashboards that actually serve your needs, and advanced strategies to transform raw data into profitable decisions. Ready to let your numbers work harder for you? Let’s dive in.
The role of data in e-commerce success
Data isn’t just a byproduct of your store’s operation – it’s the compass that should guide every significant business decision you make. When leveraged correctly, analytics become your competitive edge in an increasingly crowded marketplace.
Driving informed decision-making
Gut feelings might get you started, but data keeps you on the right path. For a dropshipper trying to decide which products to list next, historical performance data across similar items can mean the difference between wasted ad spend and your next bestseller. For inventory-based stores, precise sales velocity data might mean avoiding thousands in deadstock or preventing costly stockouts during peak seasons.
Consider this: a study from the Journal of E-Commerce Research found that Shopify stores using data-driven decision frameworks saw an average 23% higher profit margin than those relying primarily on intuition. Your competition is likely already using these insights against you.
Optimizing operations and profitability
Beyond product selection, analytics drive operational improvements that compound over time. Small efficiency gains – a 2% improvement in conversion rate, a 5% reduction in return rates, a 10% faster fulfillment process – might seem modest in isolation. Combined, they can transform your profitability.
For both business models, analytics reveal inefficiencies that drain resources. But the specific metrics that matter will vary dramatically based on whether you’re dropshipping or managing inventory directly.
Unique challenges of dropshipping vs. inventory-based stores
Inventory management differences
Dropshippers face the paradox of selling inventory they never physically handle. This creates unique analytics challenges around stock accuracy and availability. When your supplier runs out of stock, how quickly do you know? Does your Shopify store automatically reflect these changes? The best dropshippers build systems that track supplier inventory levels in near real-time.
Inventory-based stores, by contrast, need analytics that optimize carrying costs against stockout risks. Their data must answer precise questions: “How much inventory should we hold for each SKU? When exactly should we reorder? Which products tie up the most capital for the least return?”
Supply chain considerations
Your supply chain structure fundamentally changes which analytics matter most. Dropshippers need visibility into supplier performance across fulfillment speed, order accuracy, and product quality. When you’re completely dependent on third parties to deliver the customer experience, measuring their performance becomes critical.
For inventory-based stores, the supply chain analytics focus internally on warehouse operations, picking efficiency, packaging costs, and shipping performance. Your data needs to highlight bottlenecks in your fulfillment process that could be costing you money or customer satisfaction.
Customer experience factors
The customer journey differs significantly between these models, requiring different analytics approaches. Dropshippers need to carefully track shipping times and customer satisfaction metrics since these represent major vulnerability points. When shipping times from overseas suppliers stretch beyond customer expectations, data can help you proactively manage the situation.
Inventory-based stores should focus analytics on inventory availability, same-day fulfillment rates, and the relationship between stock levels and customer satisfaction. Your in-house control over inventory should translate to a more consistent customer experience – but only if you’re measuring the right things.
Understanding Shopify Analytics: Core Concepts
Before diving into model-specific strategies, let’s establish a foundation of what’s actually possible with Shopify’s native analytics capabilities. The platform offers powerful tools right out of the box, but knowing how to configure them for your specific business model makes all the difference.
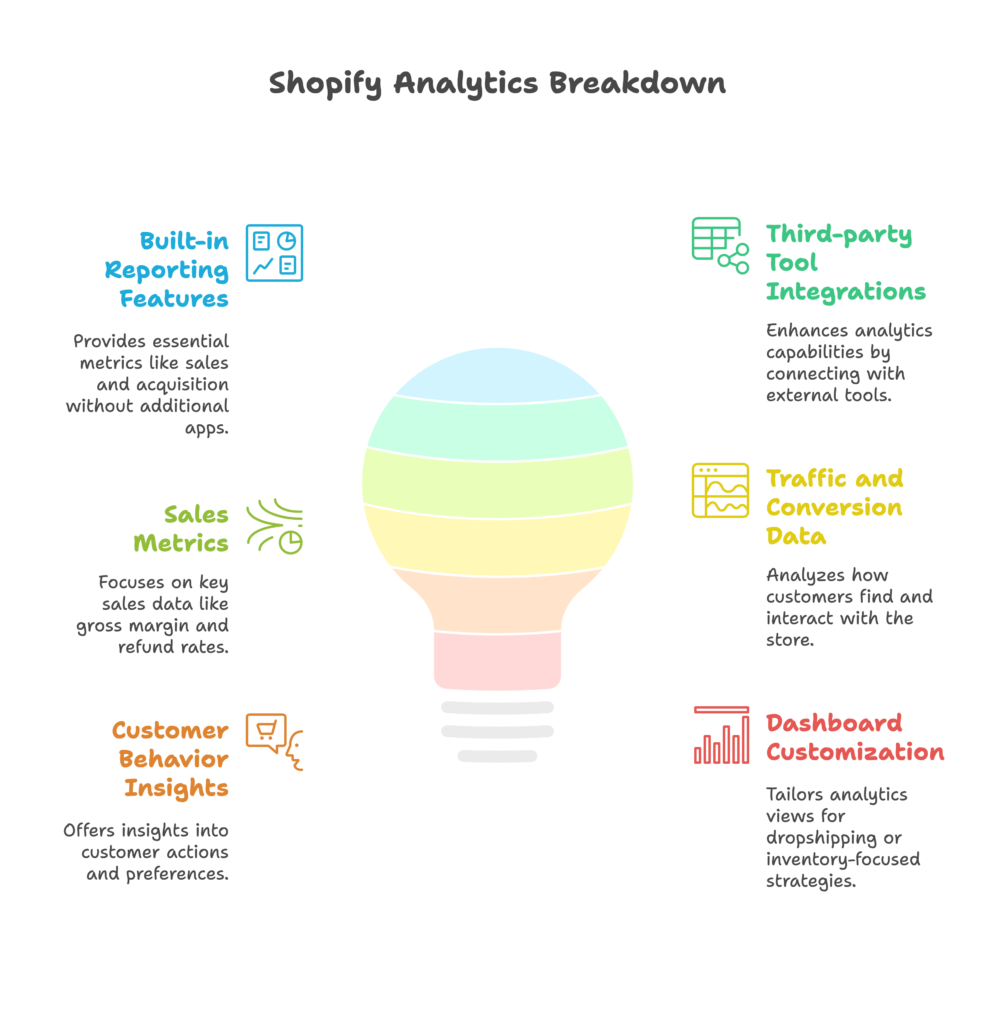
Overview of Shopify’s analytics capabilities
Built-in reporting features
Shopify’s native analytics dashboard provides immediate access to essential metrics without requiring additional apps or integrations. These built-in reports cover sales, acquisition, behavior, and marketing – giving you a solid baseline for understanding your store’s performance.
The dashboard is particularly valuable for newer store owners who might feel overwhelmed by more complex analytics platforms. You’ll find daily sales reports, acquisition metrics showing where your visitors come from, and behavior reports revealing how customers interact with your store.
What many merchants don’t realize is that the reporting capabilities expand significantly as you upgrade your Shopify plan. While Basic Shopify provides fundamental reports, Shopify and Advanced Shopify unlock professional and custom reports that allow for much deeper analysis – a crucial consideration when deciding which plan fits your analytics needs.
Integration with third-party tools
Shopify’s real analytics power comes from its extensive integration ecosystem. Whether you connect Google Analytics for more sophisticated user behavior tracking or specialized inventory management tools, these integrations extend your visibility far beyond Shopify’s native capabilities.
For dropshippers, integration with supplier systems and product research tools creates a more complete picture of your supply chain and market opportunities. Inventory-based stores benefit enormously from connecting inventory management systems that can provide more granular stock analytics than Shopify offers natively.
The key is building an integrated analytics stack where data flows seamlessly between systems without requiring manual exports and imports. This automation ensures your data is always current and frees your time for analysis rather than data collection.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) for e-commerce
Sales metrics
While both business models care about core sales metrics, the context and implications differ significantly. Beyond the obvious metrics like total sales and average order value, you should be tracking:
- Gross margin by product – Particularly important for dropshippers who may see wildly different margins across products and suppliers
- Refund and chargeback rates – Often higher for dropshippers due to quality control and shipping time issues
- Sales by traffic source – Helps both models understand which marketing channels deliver revenue, not just traffic
- Sales velocity – Critical for inventory-based stores to prevent stockouts and overstock situations
The interpretation of these metrics varies by business model. A sudden spike in sales might be pure good news for a dropshipper, but could signal inventory challenges for a store managing its own stock. Context matters enormously when reading these numbers.
Traffic and conversion data
Traffic metrics reveal how customers find and interact with your store. Both models should monitor:
- Conversion rate by traffic source – Helps identify which channels bring qualified visitors
- Device category performance – Mobile, desktop, and tablet conversion rates often vary dramatically
- Geographic data – Particularly important for dropshippers concerned with shipping times to different regions
- Cart abandonment rate – Often higher for dropshippers with longer shipping times or inventory stores with stock limitations
For dropshippers, conversion metrics need special attention as they often face trust barriers that inventory-based brands might not. Tracking how trust elements like reviews and shipping information affect conversion can be particularly revealing.
Customer behavior insights
Understanding how customers interact with your store provides invaluable insights for optimization. Pay close attention to:
- Search queries – What are visitors looking for that you might not offer yet?
- Product page bounce rates – High bounces might indicate missing information or trust elements
- Time to purchase – Dropshipping stores often see longer consideration periods due to perceived risks
- Return customer rate – Typically higher for inventory-based stores with faster shipping and consistent quality
Behavior analysis helps you understand not just what’s happening in your store, but why. This context is crucial for making meaningful improvements rather than superficial changes.
Customizing dashboards for different business models
Selecting relevant metrics for dropshipping
Dropshippers should configure their analytics dashboards to prominently feature supplier performance metrics, shipping time averages, and product-level profitability. Since your business revolves around curation and marketing rather than fulfillment, your dashboard should emphasize marketing performance and product selection effectiveness.
Create custom reports that correlate shipping times with customer satisfaction and repeat purchase rates. Set up alerts for products approaching profitability thresholds that might require price adjustments. Your dashboard should serve as an early warning system for supplier issues that could damage your customer experience.
Prioritizing inventory-focused KPIs for stocked products
For inventory-based stores, dashboards should center on stock levels, inventory turnover, and fulfillment efficiency. Create visual indicators that highlight products approaching reorder points and items with declining sales velocity that might become deadstock.
Configure reports showing the relationship between inventory levels and conversion rates – many merchants are surprised to discover that slightly higher inventory levels can significantly increase conversion by ensuring products show as “in stock” more consistently. Your dashboard needs to help you balance the contradictory goals of minimizing inventory costs while maximizing product availability.
Analytics for Dropshipping Stores on Shopify
Dropshipping presents unique analytics challenges. When you don’t physically handle products or control fulfillment, data becomes your primary tool for maintaining quality control and profitability. Let’s examine the most critical analytics areas for dropshipping operations.
Tracking supplier performance
Order fulfillment rates
Supplier reliability forms the backbone of a successful dropshipping operation. Track fulfillment rates meticulously – not just whether orders are fulfilled, but how quickly suppliers process them after receiving notification. Top-performing dropshippers set up automated tracking that flags suppliers whose fulfillment speed drops below predetermined thresholds.
Create a system to calculate the percentage of orders fulfilled within 24, 48, and 72 hours for each supplier. Suppliers consistently missing your target windows require intervention or replacement before they damage your customer experience and reputation.
Shipping times and accuracy
Shipping performance analytics should go beyond averages to identify problematic patterns. Track shipping times by destination region, supplier, product category, and shipping method. This granularity helps identify specific combinations that consistently underperform – like a particular supplier shipping to European customers, or certain product categories that face customs delays.
Equally important is delivery accuracy – what percentage of packages arrive at the correct destination on the first attempt? Shipping accuracy directly impacts customer satisfaction and return rates, making it a critical KPI for dropshipping operations.
Product quality metrics
Without physical quality control, you need proxy metrics to identify product issues before they become pattern problems. Track metrics like:
- Return rates by supplier and product – Spikes often indicate quality problems
- Negative review mentions by topic – Categorize mentions of “poor quality,” “not as described,” etc.
- Customer service contacts by product – Products generating excessive support tickets warrant investigation
- Repeat purchase rates – Low repurchase rates may signal dissatisfaction with product quality
The most successful dropshippers create early warning systems that flag quality issues after just a handful of problems rather than waiting for statistically significant samples. Catching issues early preserves customer trust and prevents revenue losses.
Managing product listings and pricing
Monitoring competitor pricing
Price sensitivity is particularly acute in dropshipping markets, where many sellers may offer identical products. Implement automated price monitoring for your top-selling items to track how your pricing compares to competitors. This data helps you find the optimal balance between competitive pricing and profitability.
Don’t just track the base price – monitor competitors’ shipping costs, guarantees, and special offers that might make their total value proposition more attractive despite a higher sticker price. Your analytics should provide a complete competitive picture, not just price points in isolation.
Analyzing product performance across suppliers
When you have the option to source similar products from different suppliers, comparative performance analytics become crucial. Track metrics like profit margin, fulfillment speed, return rates, and customer satisfaction across suppliers offering comparable products.
This analysis often reveals that the supplier with the lowest wholesale price isn’t necessarily the most profitable when all factors are considered. A slightly more expensive supplier with faster shipping, better quality control, and fewer customer service issues frequently delivers better overall profitability.
Identifying trending products for quick addition
Successful dropshipping relies on quickly identifying and listing trending products before they reach market saturation. Develop analytics that track:
- Search volume trends for relevant keywords
- Social media mention growth for product categories
- Supplier inventory changes that might indicate increasing demand
- Competitor new product additions in your niche
The most sophisticated dropshippers create scoring systems that combine these factors to generate “trend potential” scores for new product opportunities. This data-driven approach to product selection typically outperforms intuition-based methods.
Customer acquisition and retention analytics
Marketing channel effectiveness
For dropshippers, marketing effectiveness directly impacts profitability since you can’t compete on fulfillment speed or exclusive products. Your analytics should provide granular visibility into which marketing channels deliver not just traffic, but purchasing customers with the highest lifetime value.
Go beyond simple attribution to understand how channels interact. Multi-touch attribution models often reveal that channels appearing ineffective in last-click analysis actually play crucial roles in the customer journey. This nuanced understanding prevents cutting channels that appear unprofitable but actually contribute significantly to conversion.
Customer lifetime value in dropshipping context
Customer lifetime value (CLV) calculations need special consideration in dropshipping businesses. The model typically faces higher customer acquisition costs and lower repeat purchase rates than inventory-based stores, making accurate CLV calculation crucial for sustainable growth.
Your CLV analytics should segment customers by acquisition channel, first product purchased, geographic region, and other relevant factors. These segments often show dramatic CLV variations that should inform your product selection and marketing investment decisions.
Return rates and reasons
Return analytics provide a goldmine of product and supplier insights for dropshippers. Track return rates at the product, supplier, and category levels to identify problem areas. More valuable still is analyzing return reasons – create categorized data on why customers return products to spot patterns that might indicate supplier issues.
Sophisticated dropshippers compare their return rates to industry averages for similar products. This context helps determine whether elevated return rates reflect supplier problems or are simply normal for that product category.
Inventory-Based Store Analytics on Shopify
Managing your own inventory introduces a different set of analytics challenges and opportunities. When you control the entire fulfillment process, your data can drive efficiency at every stage – but only if you’re measuring the right things. Let’s explore the analytics that matter most for inventory-based Shopify stores.
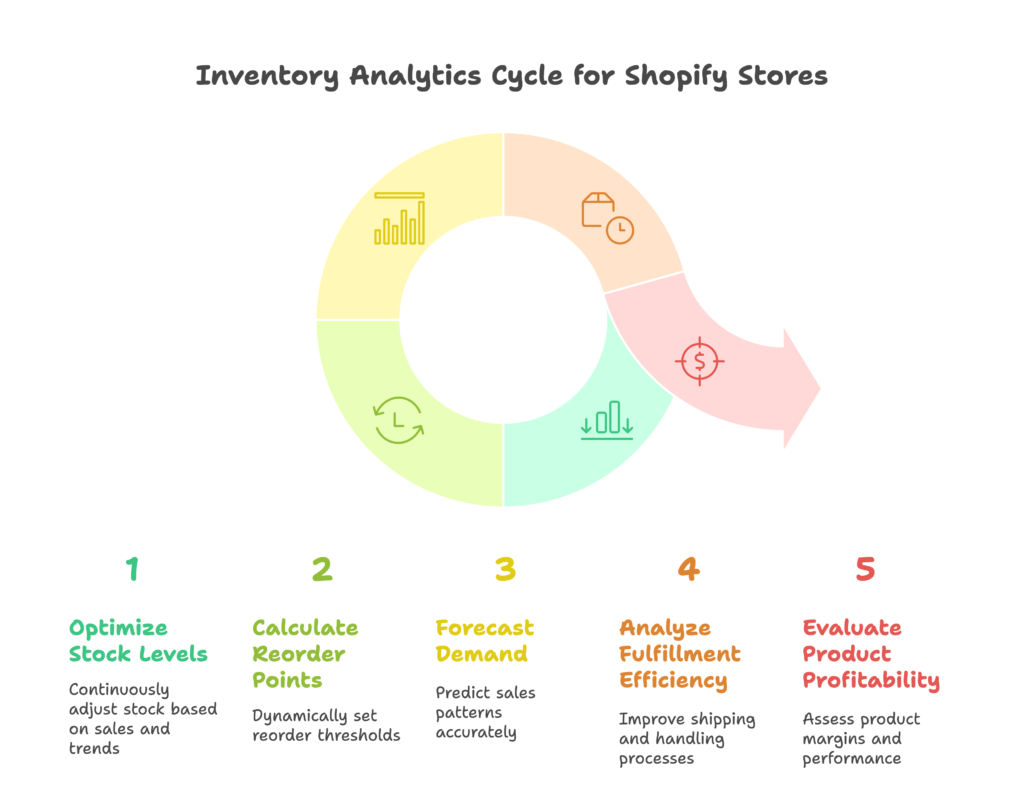
Stock level optimization
Inventory turnover rates
Inventory turnover – how quickly you sell through your stock – directly impacts cash flow and profitability. Calculate this metric at the product, category, and overall inventory levels to identify where your capital is moving efficiently and where it’s getting trapped in slow-moving stock.
While high turnover generally indicates healthy inventory management, context matters. Seasonal products naturally have different turnover patterns than staples. Luxury items typically turn over more slowly than consumables. Your analytics should compare turnover rates against appropriate benchmarks for each product type rather than applying one-size-fits-all targets.
Reorder point calculations
Sophisticated inventory analytics go beyond simple reorder points based on fixed time periods. Your system should calculate dynamic reorder points that account for:
- Current sales velocity – How quickly the product is selling now
- Historical seasonality – How sales patterns typically change throughout the year
- Supplier lead times – How long it takes to receive new inventory after ordering
- Safety stock requirements – The buffer needed to prevent stockouts
These calculations should update automatically as conditions change. A product featured in your marketing or experiencing unexpected virality needs adjusted reorder points reflecting its new sales velocity.
Seasonal demand forecasting
For inventory-based stores, accurate seasonal forecasting can mean the difference between capitalizing on peak demand and drowning in excess inventory (or missing sales due to stockouts). Your analytics should clearly display year-over-year seasonal patterns at the product and category level.
Go beyond simple “holiday season” analysis to identify micro-seasonal trends specific to your products. Many inventory-based merchants discover highly profitable ordering patterns by detecting seasonal trends that competitors miss, allowing them to stock up before suppliers raise prices to meet industry-wide demand spikes.
Warehouse and fulfillment efficiency
Pick, pack, and ship times
Your fulfillment process contains hidden costs and opportunities that only proper analytics can reveal. Track the time required for each fulfillment stage: picking products from shelves, packing orders, and preparing shipments. Breaking down the process highlights bottlenecks and improvement opportunities.
Time tracking often reveals surprising inefficiencies. Perhaps certain product combinations consistently take longer to pick due to warehouse layout. Maybe specific packaging requirements create slowdowns. These insights let you reorganize your warehouse, adjust staffing, or reconsider packaging to improve efficiency.
Inventory accuracy metrics
The gap between your system’s inventory count and physical inventory represents a critical metric for inventory-based operations. Track accuracy rates through regular cycle counts rather than waiting for annual inventories to reveal discrepancies.
Analyze patterns in inventory discrepancies – do certain products consistently show count problems? Do discrepancies increase during specific operational conditions like high-volume periods or when specific staff members work? These patterns often point to process improvements that can significantly improve inventory accuracy.
Storage cost analysis
Storage costs represent a major expense for inventory-based businesses, yet many merchants lack analytics that properly attribute these costs to specific products. Develop metrics that calculate the true storage cost per product based on:
- Physical space required – Both footprint and height utilization
- Storage duration – How long products typically remain in inventory
- Special requirements – Climate control, security, or other special storage needs
This analysis frequently identifies products whose profitability looks solid on paper but becomes questionable when storage costs are properly attributed. It also helps optimize warehouse layout by revealing which products deserve premium positions based on turnover and picking frequency.
Product performance and profitability
Gross margin by SKU
For inventory-based stores, gross margin analysis needs to incorporate all inventory-related costs to provide an accurate profitability picture. Your analytics should calculate margins that include:
- Product cost – The direct cost of purchasing the inventory
- Shipping to your warehouse – Inbound freight costs
- Storage costs – As discussed above
- Handling costs – Labor for receiving, stocking, and managing inventory
- Shrinkage – Inventory loss through damage, theft, or discrepancies
This true margin calculation often reshuffles which products appear most profitable, leading to better inventory investment decisions and more accurate pricing.
Slow-moving inventory identification
Slow-moving inventory ties up capital and space that could be used more productively. Your analytics should automatically flag products whose sales velocity has dropped below profitable thresholds or deviates significantly from forecasts.
Beyond simple identification, sophisticated systems calculate the carrying cost of continuing to hold slow-moving inventory versus discounting it for faster turnover. This analysis helps make objective decisions about when to discount, bundle, or otherwise liquidate inventory that’s tying up resources.
Bundle and upsell effectiveness
For inventory-based stores, product bundling and upselling represent powerful tools for increasing average order value and moving slower inventory. Track the performance of different bundle combinations and upsell offers to identify which pairings resonate with customers.
Your analytics should compare the performance of products sold individually versus within bundles. This comparison often reveals complementary products that sell poorly alone but significantly boost the conversion rate and perceived value of other items when bundled together.
Comparative Analysis: Dropshipping vs. Inventory-Based Metrics
Understanding the fundamental differences in how these business models perform can help you make strategic decisions about your store’s direction. Let’s directly compare how key metrics typically differ between dropshipping and inventory-based Shopify stores.
Profit margin analysis
Cost structures for each model
The cost structure differences between these models directly impact how you should interpret margin metrics. Dropshipping typically features:
- Higher per-product costs (suppliers build in their profit)
- Higher shipping costs (often shipped individually from suppliers)
- Lower overhead (no warehouse, minimal inventory management)
- Higher marketing costs (more needed to differentiate non-exclusive products)
Inventory-based stores generally show:
- Lower per-product costs (volume purchasing power)
- Lower shipping costs (consolidated shipping, better carrier rates)
- Higher overhead (warehouse costs, inventory management systems)
- Lower marketing costs (easier to differentiate with service and availability)
These structural differences mean raw margin comparisons can be misleading. A dropshipper showing 25% margins might actually be more profitable than an inventory-based operation showing 35% margins when overhead is considered. Your comparative analysis needs to account for these fundamental differences.
Pricing strategy implications
Your business model directly influences your pricing flexibility and strategy. Dropshippers typically face tighter pricing constraints – they’re selling products available elsewhere, often without the fastest shipping. Their analytics should focus on finding price points that balance competitiveness with acceptable margins.
Inventory-based stores generally enjoy more pricing flexibility due to potential exclusivity, faster shipping, and better customer service. Their analytics should explore price elasticity – how sales volume responds to price changes – to find optimal price points that maximize total profit rather than per-unit margins.
Cash flow management
Working capital requirements
The cash flow profiles of these business models differ dramatically. Dropshipping requires minimal upfront investment – you generally pay suppliers after customers pay you. This creates a fundamentally different cash conversion cycle than inventory-based operations.
Inventory-based stores must closely monitor metrics like Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO) – how long inventory stays on shelves before selling. This directly impacts how much capital remains tied up in inventory. Dropshippers should instead focus on metrics around customer payment processing speed and supplier payment terms.
Payment terms and cash conversion cycle
Your cash conversion cycle – the time between paying for inventory and collecting from customers – represents a critical difference between these models. Analytics should track:
For dropshippers:
- Time between customer payment and supplier payment
- Payment processor holding periods
- Chargeback and refund rates (which claw back received funds)
For inventory-based stores:
- Days between inventory purchase and sale
- Supplier payment terms and early payment discount opportunities
- Inventory turnover by category and SKU
These metrics help optimize cash management strategies appropriate to your specific business model.
Scalability metrics
Growth rate sustainability
Both models face different constraints when scaling rapidly. Dropshippers need analytics tracking:
- Supplier capacity limitations
- Customer service load as order volume increases
- Marketing cost inflation in competitive niches
Inventory-based stores should monitor:
- Warehouse capacity utilization
- Capital requirements for inventory expansion
- Fulfillment throughput limitations
These constraints determine your sustainable growth rate – how quickly you can expand without breaking your operational model. Growth beyond this rate typically requires significant structural changes like adding suppliers (dropshipping) or expanding warehouse space (inventory-based).
Operational efficiency at different volumes
Both models experience different efficiency dynamics as they scale. Inventory-based operations often become more efficient at higher volumes due to better supplier terms, more efficient warehouse utilization, and shipping volume discounts. Their analytics should identify these efficiency thresholds to inform growth planning.
Dropshipping operations may actually face declining efficiency at scale as they outgrow reliable suppliers and face increasing customer service demands. Their analytics should monitor these inflection points where adding team members or developing supplier redundancy becomes necessary.
Advanced Analytics Strategies for Both Models
Regardless of your business model, certain advanced analytics approaches can elevate your decision-making and competitive advantage. Let’s explore sophisticated strategies that apply to both dropshipping and inventory-based operations.
Implementing predictive analytics
Demand forecasting techniques
Moving beyond historical analysis to predictive forecasting represents a significant competitive advantage. Both business models benefit from demand prediction, though the applications differ:
For dropshippers, accurate demand forecasting helps:
- Identify trending products before they peak
- Negotiate better terms with suppliers before demand surges
- Prepare marketing campaigns to capitalize on predicted trends
For inventory-based stores, demand prediction directly impacts:
- Inventory purchasing decisions
- Warehouse staffing and space allocation
- Cash flow management and financing needs
While sophisticated predictive models once required data science expertise, tools like ShopifyQL (discussed below) now make basic predictive analytics accessible to merchants without technical backgrounds.
Customer churn prediction
Identifying customers at risk of abandoning your store before they actually leave allows for proactive retention efforts. Develop analytics that flag churn risk factors like:
- Declining purchase frequency
- Decreasing average order value
- Support interactions expressing dissatisfaction
- Cart abandonment after being a loyal customer
- Reduced engagement with marketing communications
Use these signals to trigger personalized retention campaigns before customers fully disengage. For dropshippers, churn prediction is particularly valuable given the typically higher customer acquisition costs relative to lifetime value.
Lifetime value projection
Standard CLV calculations look backward at historical customer value. Advanced analytics project future value based on purchase patterns, allowing for more accurate customer acquisition budget decisions.
Your LTV projections should account for model-specific factors. Dropshippers should factor in product discovery patterns – how customers who start with certain products tend to explore your catalog. Inventory-based stores should incorporate seasonal purchasing patterns and product lifecycle considerations.
Leveraging Shopify’s data exploration tools
Building custom reports
Shopify’s custom report builder (available on higher-tier plans) allows you to create tailored analytics views addressing your specific business questions. Both models benefit from custom reports, though the focus typically differs:
Dropshippers often create custom reports around:
- Supplier performance comparisons
- Product profitability after accounting for returns and customer service
- Geographic performance correlated with shipping times
Inventory-based stores frequently build reports centered on:
- Inventory efficiency metrics
- Fulfillment performance analytics
- Product category performance relative to storage costs
The most valuable custom reports often combine data points that don’t appear together in standard reports, revealing correlations that drive strategic insights.
Using ShopifyQL for advanced queries
ShopifyQL represents Shopify’s query language for advanced data exploration. While it requires a slightly steeper learning curve than the standard analytics dashboard, it enables significantly more powerful analysis. Both business models can leverage ShopifyQL to:
- Create complex segments based on multiple conditions
- Analyze trends with sophisticated time comparisons
- Generate custom calculations not available in standard reports
- Export specialized datasets for further analysis
The investment in learning ShopifyQL pays particular dividends when diagnosing complex business challenges that standard reports can’t adequately address. Even basic ShopifyQL knowledge can uncover insights that standard analytics might miss entirely.
Integrating with business intelligence platforms
For the most advanced analytics needs, integrating Shopify with dedicated business intelligence (BI) platforms like Tableau, Power BI, or Looker provides unmatched analytical capabilities. This approach makes sense when:
- Your store generates significant data volume
- You need to combine Shopify data with external data sources
- Your analysis requires sophisticated statistical methods
- Multiple team members need customized analytics views
Both business models benefit from BI integration, though the specific implementations typically differ based on which external data sources matter most – supplier systems for dropshippers, inventory and warehouse management systems for inventory-based stores.
Multi-channel analytics integration
Consolidating data from various sales channels
As your business expands beyond your Shopify store to marketplaces like Amazon, eBay, or social commerce platforms, consolidated analytics become essential. Develop systems that combine data across all channels to provide:
- Unified sales and inventory visibility (especially crucial for inventory-based stores)
- Customer behavior insights across channels
- Profitability comparisons accounting for channel-specific fees and requirements
This consolidated view prevents the common pitfall of optimizing each channel in isolation, potentially at the expense of overall business performance.
Analyzing channel performance and attribution
Different channels typically perform differently for various product types and customer segments. Your cross-channel analytics should identify:
- Which products perform best on each channel
- How customer acquisition costs compare across platforms
- Which channels attract first-time buyers vs. repeat customers
- How return rates and customer satisfaction vary by channel
These insights inform channel-specific strategies – perhaps certain products should be exclusive to your Shopify store while others perform better on marketplaces. Both business models benefit from this analysis, though inventory-based stores must also consider channel-specific fulfillment requirements in their analysis.
Optimizing omnichannel strategies
The most sophisticated analytics approach views channels not as separate silos but as complementary touchpoints in a unified customer journey. Track how customers move between channels – perhaps discovering products on Instagram, researching on your Shopify store, and ultimately purchasing through Amazon for the shipping benefits.
This journey mapping reveals opportunities to optimize the omnichannel experience, like featuring Amazon reviews on your Shopify product pages or creating Instagram content that addresses questions typically asked by marketplace customers. For inventory-based stores, journey mapping also informs inventory allocation decisions across channels.
Actionable Insights and Implementation
Analytics only create value when translated into concrete business actions. Let’s explore how to implement effective analytics workflows and decision frameworks for both dropshipping and inventory-based Shopify stores.
Setting up analytics workflows
Daily, weekly, and monthly review processes
Establish structured review cadences appropriate to your business rhythm and model. While each business has unique needs, effective analytics review cycles typically include:
Daily reviews (15-30 minutes):
- For dropshippers: Order volumes, product performance, customer service issues
- For inventory-based stores: Inventory alerts, fulfillment performance, sales by category
Weekly reviews (30-60 minutes):
- For dropshippers: Supplier performance, marketing channel effectiveness, trending products
- For inventory-based stores: Inventory turnover, reorder planning, warehouse efficiency
Monthly reviews (1-2 hours):
- For dropshippers: Profitability analysis, supplier relationship assessment, market trend analysis
- For inventory-based stores: Storage cost optimization, product line performance, cash flow planning
These structured reviews ensure data regularly translates to action rather than accumulating unused.
Automated alerts and reporting
Develop automated alert systems that proactively notify you of conditions requiring immediate attention. These alert triggers should reflect your business model’s critical factors:
For dropshippers, critical alerts might include:
- Supplier fulfillment time exceeding thresholds
- Products experiencing sudden return rate increases
- Significant competitor price changes
For inventory-based stores, priority alerts typically center on:
- Inventory approaching reorder points
- Fulfillment falling behind schedule
- Products at risk of becoming deadstock
Configure these alerts to reach the right team members through appropriate channels – email for non-urgent matters, SMS or instant messaging for truly time-sensitive issues.
Team roles and responsibilities for data analysis
As your store grows, clearly defined analytics responsibilities become essential. Consider these role allocations:
- Store owner/manager: Strategic analytics review, KPI setting, major decision approval
- Marketing team: Channel performance, customer acquisition metrics, conversion optimization
- Operations team: For dropshippers – supplier performance; for inventory-based – fulfillment and inventory metrics
- Customer service: Customer satisfaction analytics, return reason analysis, feedback trends
Each role should have clearly defined metrics they “own,” along with action thresholds that empower decision-making without constant approval cycles. This distribution prevents analytics bottlenecks while maintaining accountability.
Data-driven decision-making framework
Hypothesis testing for business changes
Develop a structured approach to testing business hypotheses rather than making changes based on hunches. A simple but effective framework includes:
- Hypothesis formulation: Clearly state what you believe will happen and why
- Success metric definition: Identify specific, measurable outcomes that would confirm or reject your hypothesis
- Test design: Create a controlled experiment with defined variables
- Implementation: Run the test while minimizing external factors that could skew results
- Analysis: Evaluate results against your success metrics
- Decision: Implement, adjust, or abandon the change based on results
This methodical approach prevents the common pitfall of making multiple simultaneous changes that make it impossible to determine what actually worked.
A/B testing strategies on Shopify
A/B testing represents a powerful tool for both business models, though testing priorities typically differ:
Dropshippers often prioritize A/B testing:
- Product page layouts emphasizing trust elements
- Shipping information presentation to manage expectations
- Price points and discount strategies
Inventory-based stores frequently test:
- Inventory display strategies (“5 left in stock” vs. simple “in stock”)
- Shipping speed promotions
- Cross-sell and upsell presentations
Whichever elements you test, maintain experimental discipline – change only one variable at a time, ensure sufficient sample sizes for statistical significance, and document results thoroughly for future reference.
Continuous improvement cycles
Establish a formalized continuous improvement process using analytics to identify opportunities, prioritize efforts, and measure results. An effective cycle includes:
- Performance review: Regular analysis of KPIs against targets
- Gap identification: Pinpointing specific metrics falling short of goals
- Root cause analysis: Determining underlying reasons for performance gaps
- Improvement planning: Developing specific action plans with measurable outcomes
- Implementation: Executing improvements with clear ownership and timelines
- Results measurement: Tracking the impact of changes on target metrics
- Standardization: Documenting successful approaches for consistent application
This structured approach prevents the “flavor of the month” improvement pattern that often fails to create lasting change.
Privacy and data security considerations
Compliance with data protection regulations
As your analytics capabilities grow more sophisticated, data privacy compliance becomes increasingly important. Both business models need to ensure their analytics practices comply with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and emerging privacy frameworks.
Conduct regular compliance reviews of your analytics systems, addressing:
- Data collection consent mechanisms
- Personal information storage and security
- Data retention policies and implementation
- Customer data access and deletion capabilities
While compliance requirements are largely similar across business models, dropshippers face additional considerations around sharing customer data with suppliers in different jurisdictions.
Ethical use of customer data
Beyond legal compliance, ethical data use builds customer trust and protects your brand reputation. Develop clear ethical guidelines for analytics, addressing questions like:
- How granular should customer segmentation be without becoming invasive?
- What forms of behavioral prediction and influence are appropriate?
- How transparent should you be about data collection and usage?
- What safeguards prevent discriminatory outcomes in automated decisions?
Both business models benefit from ethical data practices, though inventory-based stores with higher customer loyalty and retention often have more to lose from perceived ethical breaches.
Shopify’s data handling policies and best practices
Leverage Shopify’s built-in compliance features while understanding their limitations. Familiarize yourself with how Shopify handles:
- Customer data storage and security
- Analytics data retention and anonymization
- Third-party app data access and permissions
- International data transfer considerations
Both business models should regularly audit installed apps for data access permissions, removing unnecessary access and discontinuing apps that request excessive data relative to their functionality.
References
- Shopify. (2024). “Shopify Analytics.” Shopify Help Center. https://help.shopify.com/en/manual/reports-and-analytics/shopify-analytics
- Johnson, A. (2024). “E-commerce Analytics: A Comprehensive Guide for Online Retailers.” Journal of E-Commerce Research, 15(2), 78-95.
- Smith, B. (2025). “Dropshipping vs. Inventory-Based E-commerce: A Comparative Analysis.” International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 53(4), 412-428.
- Shopify. (2025). “ShopifyQL Reference.” Shopify Developer Documentation. https://shopify.dev/api/shopifyql
- Brown, C. (2024). “Predictive Analytics in E-commerce: Applications and Challenges.” MIT Sloan Management Review, 65(3), 25-37.
Ready to supercharge your Shopify store’s analytics and boost sales with perfectly optimized discount campaigns? Growth Suite is a Shopify app that helps you analyze customer behavior, run effective on-site discount campaigns, and collect valuable customer emails. Its powerful AI engine even creates personalized, time-limited offers based on buying intention. Install it with a single click and start seeing results immediately!
Also don’t forget to check these articles to learn more about Shopify data and analytics;